STEMI vs NSTEMI: What's the Difference?
May 12, 2025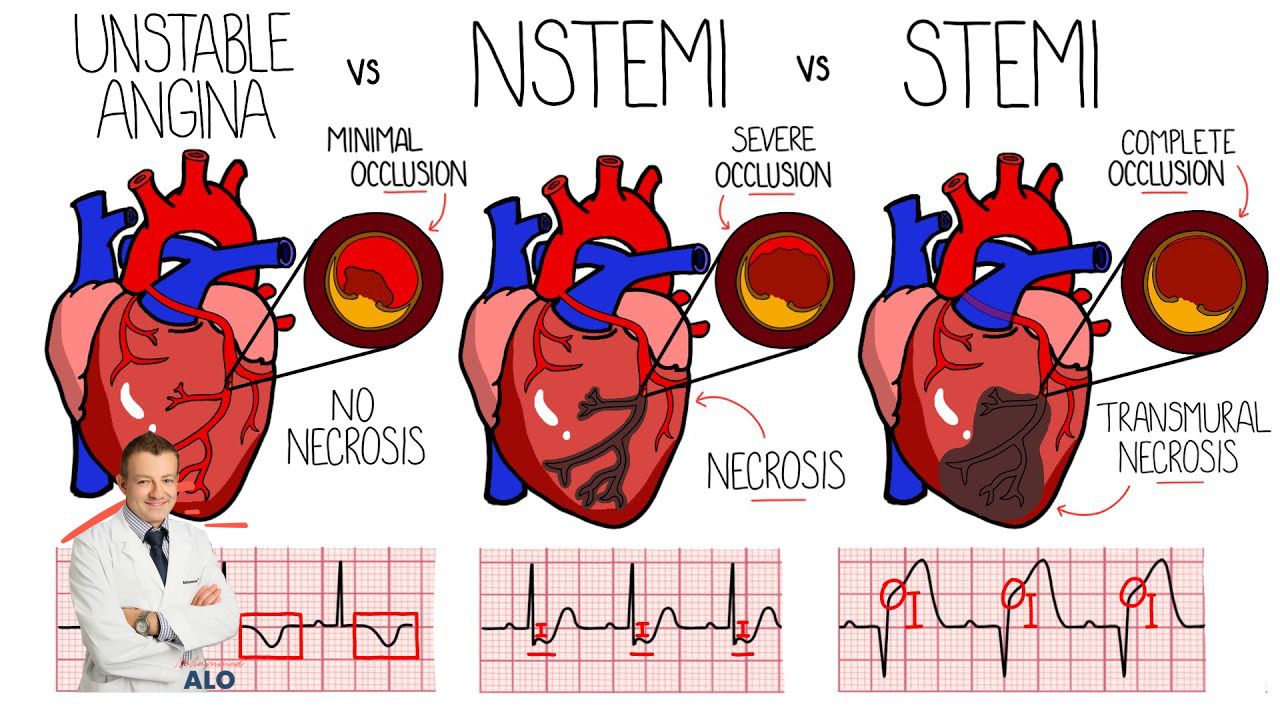
STEMI versus NSTEMI Two Very Different Types of Heart Attacks
When teaching students, residents, fellows, and other cardiologists at conferences, one of the most important concepts to understand is the treatment differences between a STEMI and an NSTEMI. Why? Because this will affect how you treat the patient. One is an emergency and the other can wait 48 to 72 hours.
ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) are types of heart attacks that occur when the blood flow to the heart is blocked, causing damage to the heart muscle. STEMI and NSTEMI are similar in that they both involve a lack of blood flow to the heart, but they differ in the extent of damage to the heart muscle and the treatments that are necessary.
What is a STEMI?
STEMI is the most severe type of heart attack, with the highest mortality rate. It occurs when there is a complete blockage of a coronary artery, leading to a lack of blood flow to a large area of the heart muscle. This results in a significant amount of damage to the heart muscle and a high risk of death.
What is a NSTEMI?
NSTEMI is a less severe type of heart attack, with a lower mortality rate than STEMI. It occurs when there is a partial blockage of a coronary artery, leading to a reduced blood flow to the heart muscle. This results in less damage to the heart muscle than in STEMI, but it is still a serious condition that requires prompt treatment.
In simple terminology, a STEMI is a complete and full occlusion of the artery while a NSTEMI is just a partial occlusion. The ST elevation is the electrical pattern on the surface ECG that develops in response to the complete occlusion. A NSTEMI does not change your surface ECG. See the pictures above.
Symptoms of STEMI vs NSTEMI?
STEMI symptoms are usually more severe and more debilitating. You usually have an acute onset, crushing chest pain or shortness of breath that is worse with exertion. People often feel a sense of doom or destruction. It's very severe.
NSTEMI will have a more insidious onset usually. With chest pain or shortness of breath that is not as severe, but still with exertion.
The symptoms of STEMI and NSTEMI are similar and may include chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, and sweating. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of these symptoms, as prompt treatment is critical in minimizing the damage to the heart muscle.
Treating STEMI vs NSTEMI
The treatment of STEMI and NSTEMI involves restoring blood flow to the heart muscle as quickly as possible. This may involve the use of medications, such as aspirin and blood-thinning drugs, as well as procedures such as angioplasty or coronary artery bypass surgery.
A STEMI is one of the few medical emergencies in medicine where a cardiologist needs to come in to open up the artery immediately. It does not matter what time of day this is.
Treatments include:
Aspirin
Brilinta/Plavix
Heparin or lovenox
Heart cath (in the case of STEMI, must be immediate)
Statin
Beta blocker
ACEI
Acute MI Studies: STEMI and NSTEMI
New data shows that not everyone may need to be on beta blockers longer depending on several factors. If the ejection fraction is below 40% then ACEIs, ARBs, ARNIs, MRA, SGLT2i, etc may be indicated.
A study published in the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) compared the effectiveness of angioplasty and coronary artery bypass surgery in the treatment of STEMI. The study followed over 4,000 participants and found that angioplasty was as effective as coronary artery bypass surgery in improving outcomes in STEMI patients.
Another study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) evaluated the effectiveness of aspirin in the treatment of NSTEMI. The study followed over 16,000 participants and found that aspirin significantly reduced the risk of death, recurrent myocardial infarction, and stroke in NSTEMI patients.
STEMI vs NSTEMI Final Words
Overall, STEMI and NSTEMI are serious conditions that require prompt treatment to minimize the damage to the heart muscle. The treatment of these conditions may involve medications and procedures such as angioplasty or coronary artery bypass surgery. By seeking medical attention immediately if you experience symptoms of a heart attack, you can significantly improve your chances of a good outcome.
Below is one of my best performing videos on YouTube, I discuss the treatment of STEMI versus NSTEMI
Feel free to shoot me questions on here or on YouTube.
Still Have Questions? Stop Googling and Ask Dr. Alo.
You’ve read the science, but applying it to your own life can be confusing. I created the Dr. Alo VIP Private Community to be a sanctuary away from social media noise.
Inside, you get:
-
Direct Access: I answer member questions personally 24/7/365.
-
Weekly Live Streams: Deep dives into your specific health challenges.
-
Vetted Science: No fads, just evidence-based cardiology and weight loss.
Don't leave your heart health to chance. Get the guidance you deserve. All this for less than 0.01% the cost of health insurance! You can cancel at anytime!
[👉 Join the Dr. Alo VIP Community Today]