No One Has Side Effects From Statins!
Feb 11, 2026
Statin Side Effects: What the Science Really Shows (And Why Most Are Rare or Not Caused by Statins)
Statins are among the most widely prescribed medications in the world, and also among the most misunderstood. The internet is full of people trying to scare you away from statins, only to turn around a sell you unregulated "statin like supplements".
Many product labels for statins (cholesterol-lowering drugs) list a long menu of scary side effects, such as memory loss, depression, and sleep problems. However, many of these warnings come from lower-quality studies where patients knew they were taking the drug, which can bias the results.
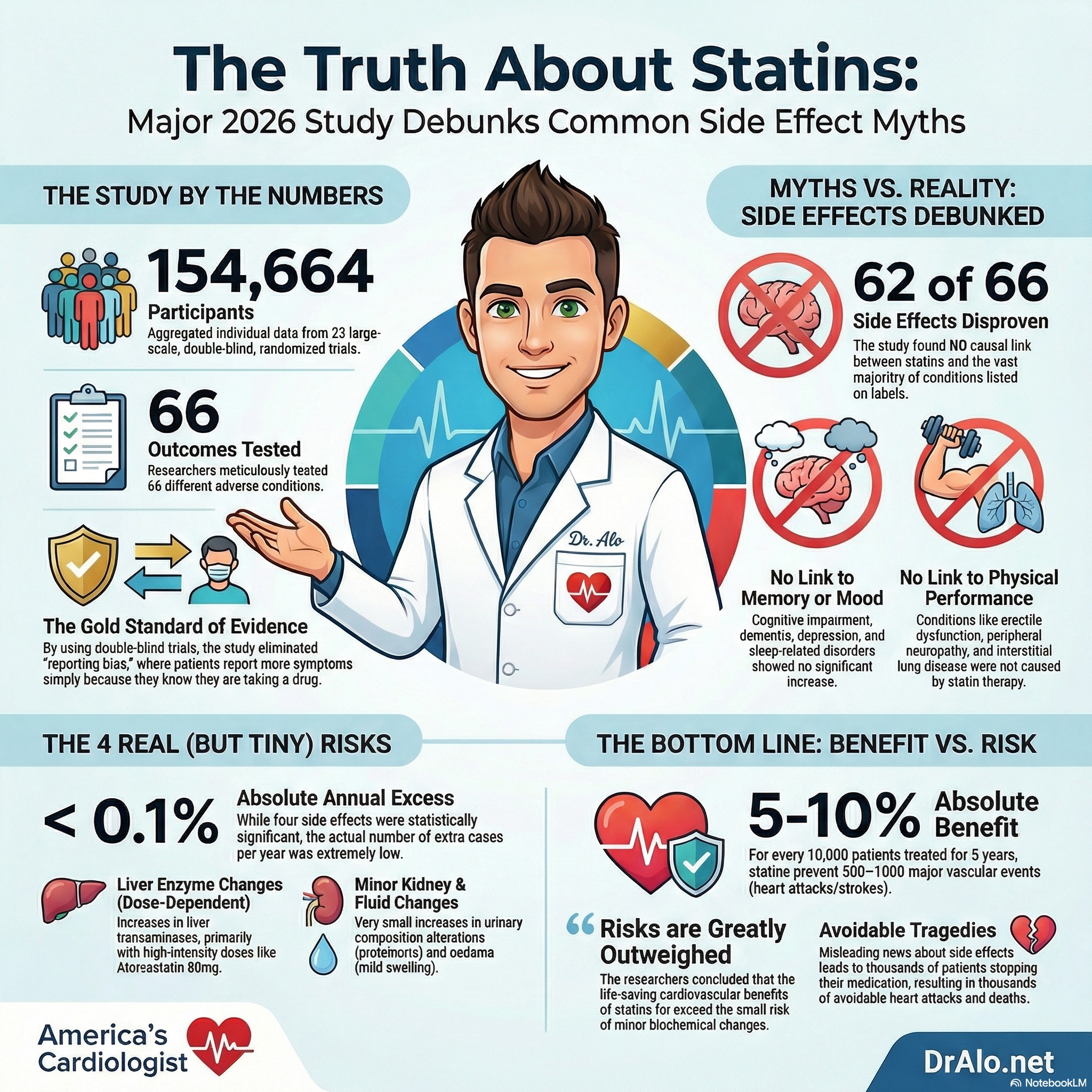
This study aimed to find the truth by looking at data from 23 large, high-quality experiments (called "double-blind randomized controlled trials") involving over 150,000 participants. In these trials, neither the patients nor the doctors knew who was taking the real drug and who was taking a dummy pill (placebo).
Key Findings: What Statins Do NOT Cause
The study found that statins did not cause most of the frightening side effects often blamed on them. Specifically, there was no evidence that statins cause:
• Memory loss or cognitive impairment
• Depression
• Sleep disturbance
• Sexual dysfunction
• Kidney injury
• Vision problems
This suggests that many symptoms people experience while taking statins might be coincidental or caused by the "nocebo effect" (expecting to feel bad because of a warning label) rather than the drug itself.
This suggests that many symptoms people experience while taking statins might be coincidental or caused by the "nocebo effect" (expecting to feel bad because of a warning label) rather than the drug itself.
Key Findings: The Actual Side Effects
While previous research had already established that statins can slightly increase the risk of muscle pain and diabetes, this new analysis identified three other specific side effects:
1. Liver Test Changes: Statins caused a small increase in irregular liver blood test results (specifically liver enzymes). This was more likely to happen with higher doses of the drug. However, there was no increase in serious liver damage or failure.
2. Swelling (Oedema): There was a very small increase in reported swelling, though it was not considered dangerous.
3. Urine Changes: There was a slight increase in reports of proteins found in urine, but this did not lead to kidney damage.
The Bottom Line
The researchers concluded that the benefits of statins—preventing heart attacks and strokes—far outweigh these small risks. They suggest that official medical labels should be updated to remove unproven side effects so that patients aren't scared away from taking life-saving medication unnecessarily
If you search online for statin side effects, you’ll quickly encounter alarming claims: memory loss, muscle damage, kidney failure, depression, sexual dysfunction, and more. Many patients stop their statin out of fear, often without discussing it with their doctor.
But what does high-quality science actually show?
A landmark 2026 analysis published in The Lancet—one of the world’s most respected medical journals—provides the clearest answer yet: most side effects commonly blamed on statins are either extremely rare or not caused by statins at all .
Let’s break this down clearly, honestly, and based on evidence—not headlines.
Why Statin Side Effects Are So Widely Misunderstood
Much of the fear around statins comes from:
- Observational studies (not randomized trials)
- Case reports
- Patient anecdotes
- Non-blinded data (patients know they’re taking a statin)
These sources are vulnerable to nocebo effects, bias, and coincidence. Many symptoms blamed on statins—fatigue, pain, memory issues—are already common in aging adults, especially those with cardiovascular risk factors.
To determine whether statins truly cause side effects, researchers must use double-blind randomized controlled trials, where neither patients nor doctors know who is receiving the drug.
That’s exactly what the Cholesterol Treatment Trialists’ (CTT) Collaboration did.
The Largest and Most Rigorous Statin Analysis Ever Conducted
The 2026 Lancet study analyzed:
- 154,664 participants
- 23 large double-blind randomized trials
- Median follow-up: nearly 5 years
- 66 different adverse outcomes listed on statin drug labels
This design eliminates expectation bias and allows researchers to determine true causation rather than coincidence .
The Key Finding: 62 of 66 “Statin Side Effects” Are NOT Caused by Statins
After controlling for multiple testing and bias, researchers found that:
Statins were NOT causally linked to 62 out of 66 adverse effects commonly listed on statin labels.
This includes no increased risk of:
- Memory loss or cognitive decline
- Dementia or Alzheimer’s disease
- Depression or mood disorders
- Sleep disturbances
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Erectile dysfunction
- Kidney failure
- Interstitial lung disease
- Sexual dysfunction
- Chronic fatigue
- Headaches or dizziness
These symptoms occurred at the same rate in people taking placebo.
In other words: statins were not the cause .
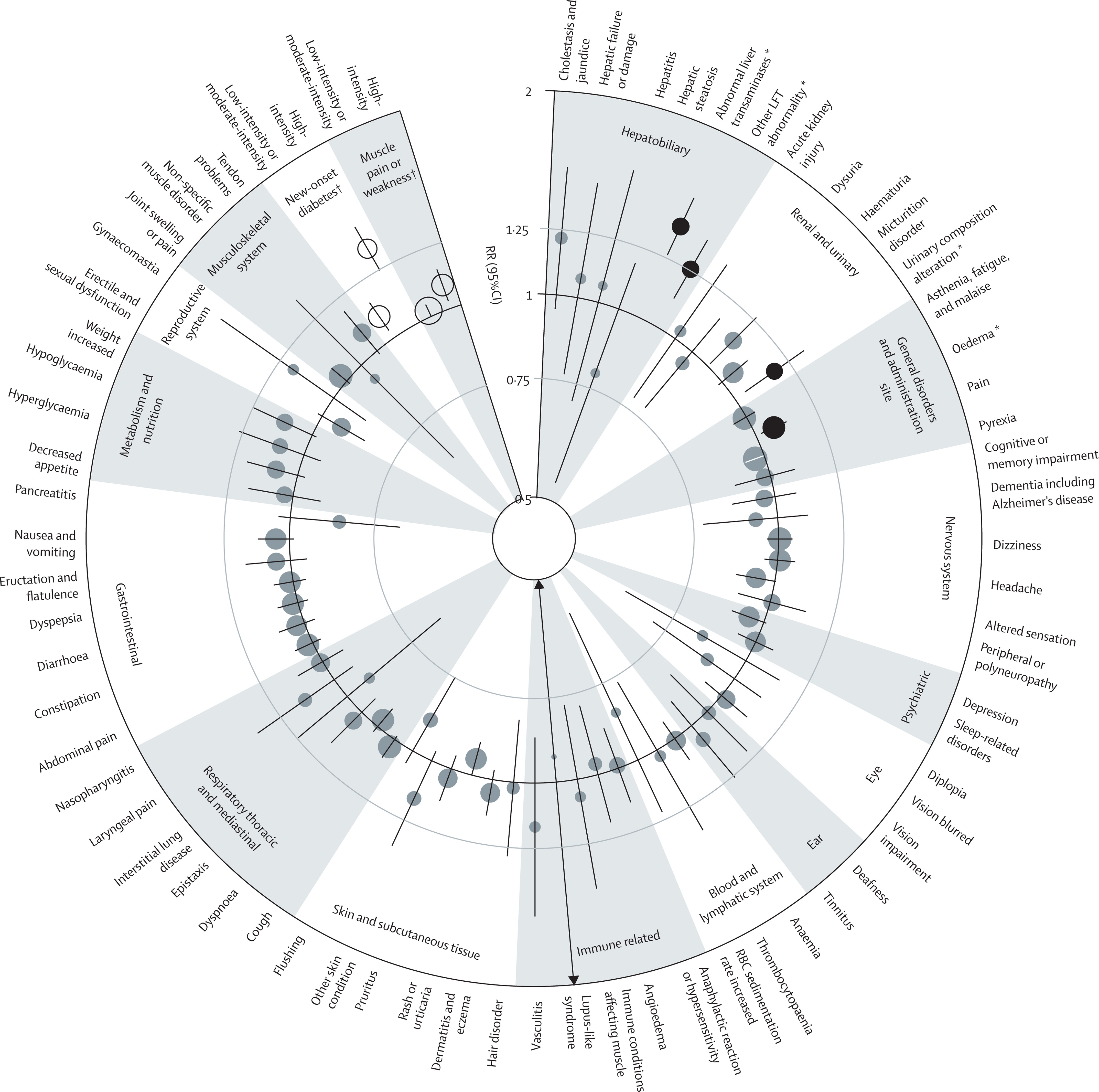
Figure 1 Effect of statin versus placebo on events listed in statin SmPCs, subdivided by component parts
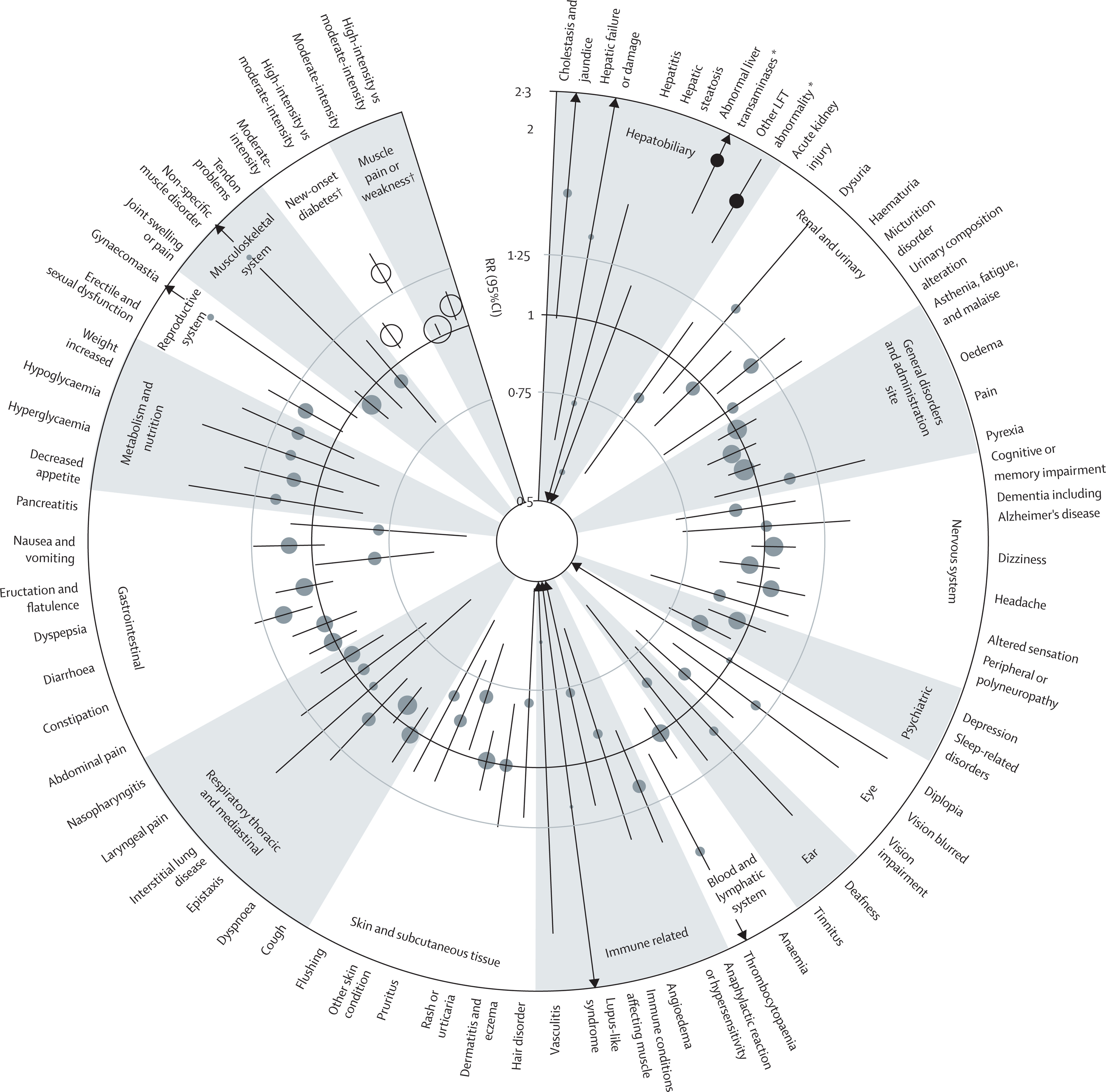
Figure 2 Effect of more intensive statin therapy versus less intensive statin therapy on events listed in statin SmPCs, subdivided by component parts
So What Statin Side Effects Are Real?
Science does not say statins have zero side effects. It says the real risks are small, specific, and measurable.
- Muscle Symptoms (Rare and Often Mild)
- Severe muscle injury (myopathy):
~1 case per 10,000 patient-years - Rhabdomyolysis (life-threatening):
~2–3 cases per 100,000 patient-years - Mild muscle aches:
Small increase, mostly in the first year
Importantly, most muscle pain reported by patients occurs just as often with placebo.
- New-Onset Diabetes (Small and Predictable)
Statins slightly increase diabetes diagnoses—but primarily in people who already had:
- Prediabetes
- Insulin resistance
- Metabolic syndrome
The absolute increase is small, and cardiovascular benefit vastly outweighs this risk.
- Liver Enzyme Elevations (Usually Clinically Insignificant)
The Lancet analysis found a small, dose-dependent rise in liver enzymes, especially with very high-dose atorvastatin.
Key points:
- Absolute annual excess: <0.1%
- No increase in liver failure
- No increase in hepatitis
- No increase in liver-related death
These lab changes are typically reversible and asymptomatic . The guidelines do not recommend checking liver function for those on statins.
What About Memory Loss and Brain Fog?
This is one of the most persistent myths.
The CTT meta-analysis found no causal relationship between statins and:
- Cognitive impairment
- Memory loss
- Dementia
In fact, several studies suggest statins may reduce stroke-related cognitive decline by preventing vascular injury to the brain.
Why Patients Feel Better When They Stop Statins (Even When Statins Aren’t the Cause)
This phenomenon is called the nocebo effect.
When patients expect harm:
- Normal aches feel worse
- Everyday fatigue feels abnormal
- Symptoms get attributed to the medication
Double-blind trials show that when patients don’t know they’re taking a statin, most symptoms disappear.
The Cost of Statin Fear Is Measured in Heart Attacks and Strokes
After negative media coverage about statins:
- Statin discontinuation increased by ~10%
- Tens of thousands stopped therapy
- Thousands of preventable heart attacks and strokes followed
This is not theoretical—it’s documented in population-level data .
The Bottom Line: Benefits Vastly Outweigh Risks
For most patients:
- Statins reduce heart attack risk by 25–35%
- Prevent strokes
- Reduce cardiovascular death
- Have a long, proven safety record
The strongest evidence available shows that:
Most statin side effects are rare, mild, or not caused by statins at all.
What Patients Should Do Instead of Stopping Statins
If symptoms occur:
- Adjust dose (various ways)
- Switch statins
- Address vitamin D deficiency
- Review drug interactions
- Rechallenge under supervision
Stopping statins without guidance is far riskier than continuing them thoughtfully.
Final Thought from Dr. Alo
Statins are not perfect—but they are one of the most effective, life-saving therapies in modern medicine.
Fear should never outweigh evidence.
And evidence has never been clearer.
Still Have Questions? Stop Googling and Ask Dr. Alo.
You’ve read the science, but applying it to your own life can be confusing. I created the Dr. Alo VIP Private Community to be a sanctuary away from social media noise.
Inside, you get:
-
Direct Access: I answer member questions personally 24/7/365.
-
Weekly Live Streams: Deep dives into your specific health challenges.
-
Vetted Science: No fads, just evidence-based cardiology and weight loss.
Don't leave your heart health to chance. Get the guidance you deserve. All this for less than 0.01% the cost of health insurance! You can cancel at anytime!
[👉 Join the Dr. Alo VIP Community Today]



















